I. The Urgent Need for Efficient Hot Repair of Refractories in Rotary Melting Furnaces
Rotary melting furnaces serve as critical thermal processing equipment in metallurgy, glass, cement, and other industries, with their operational stability directly impacting production efficiency and quality. Complex operating conditions, including prolonged high temperatures and material erosion, often cause wear and spalling of refractories inside the furnace. Traditional cold repairs require furnace shutdown and cooling, resulting in prolonged downtime, high costs, and significant energy consumption. The hot repair advantages of the Dry Gunning Machine offer a revolutionary solution to this problem, providing critical support for continuous production.
II. Dry Gunning Machine: Core Principles and Key Components
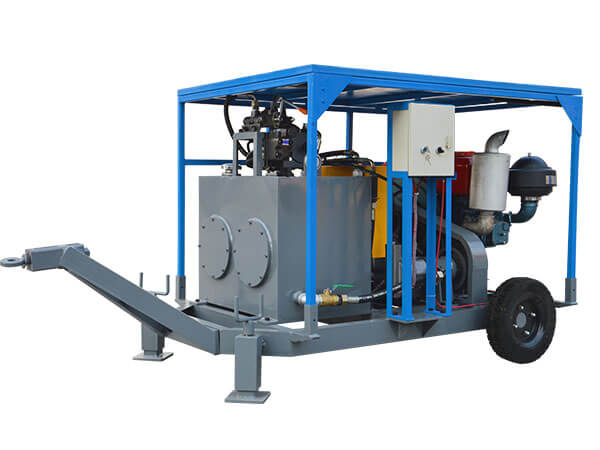
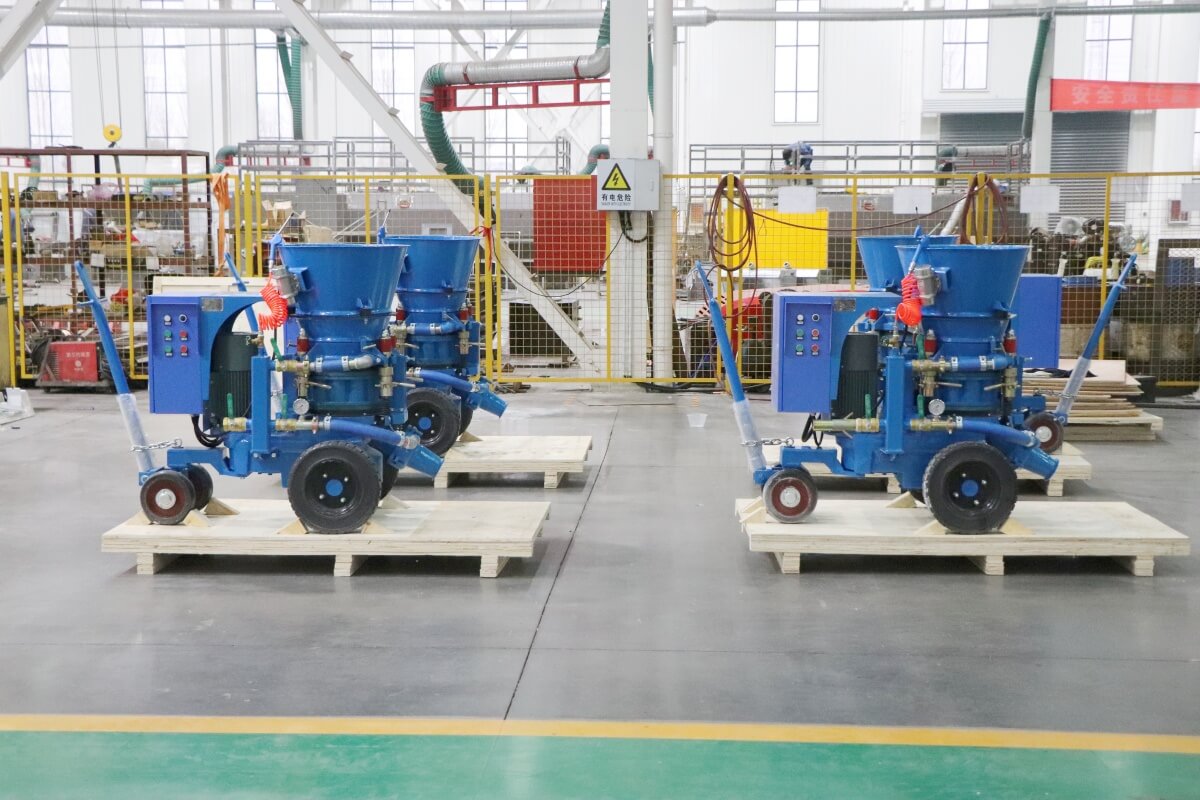
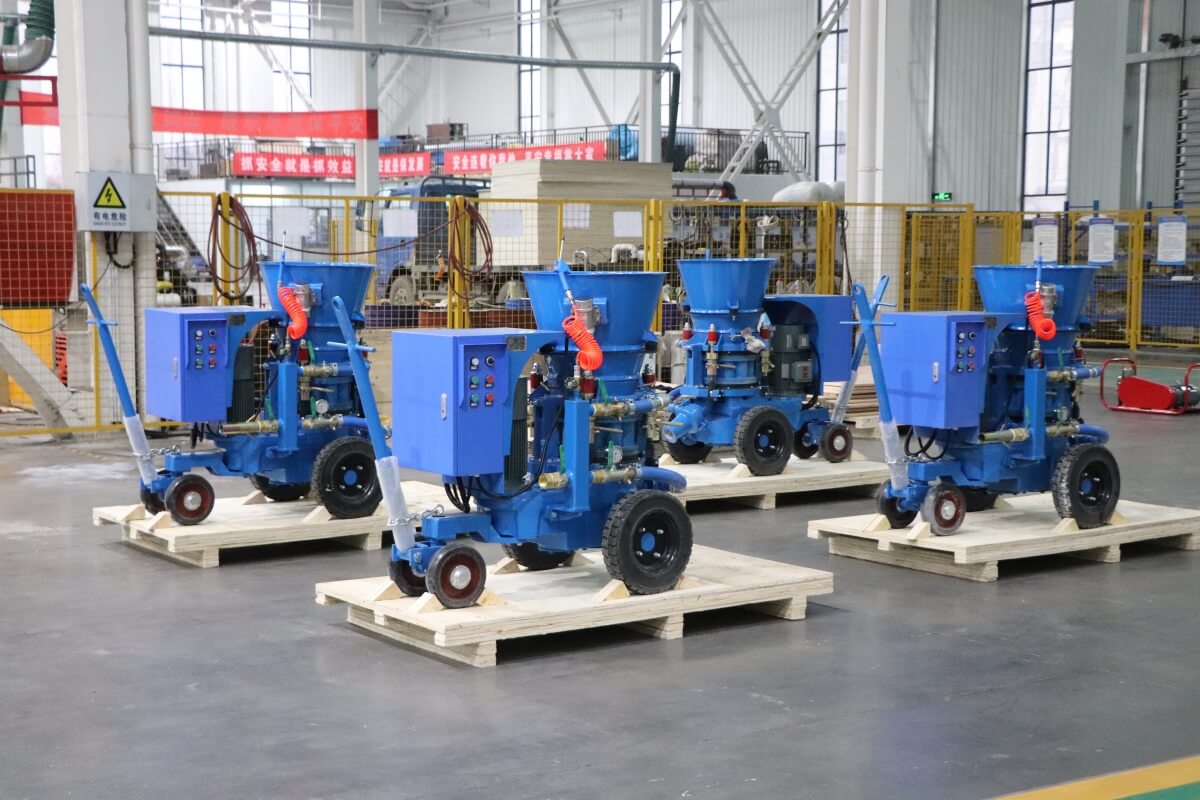
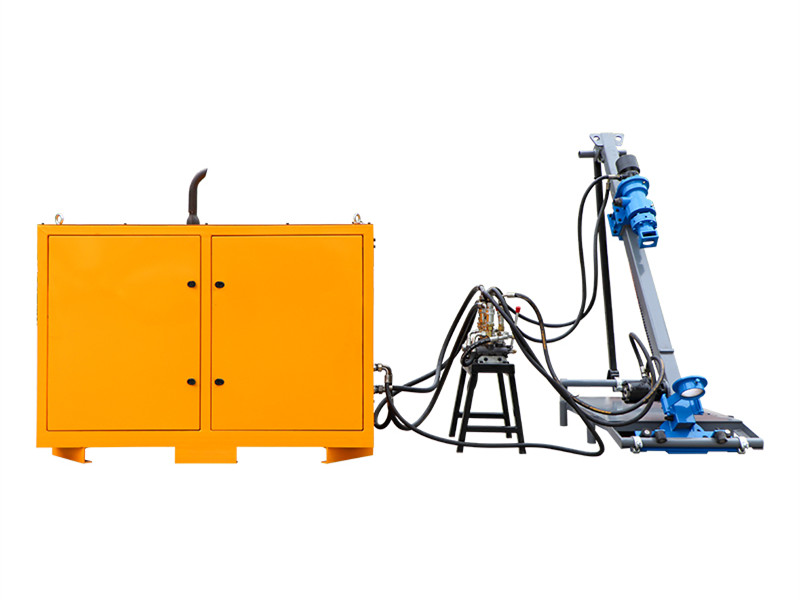
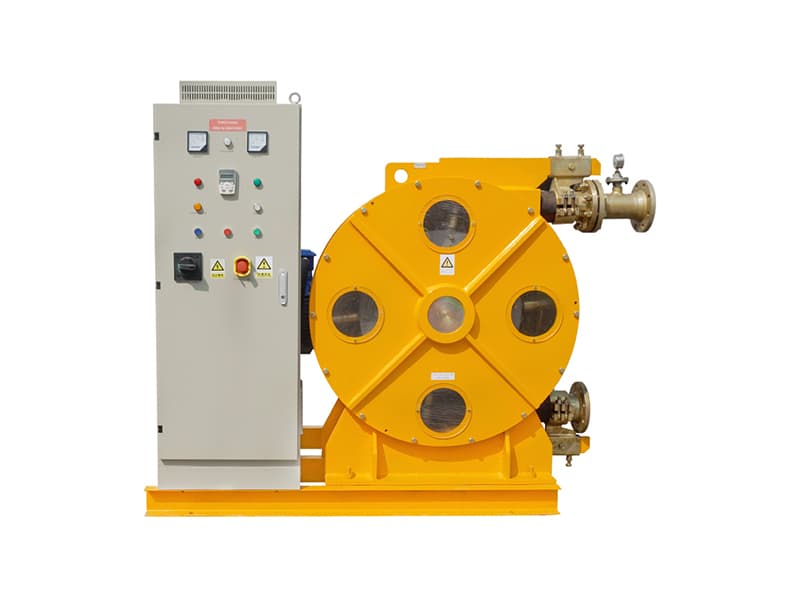
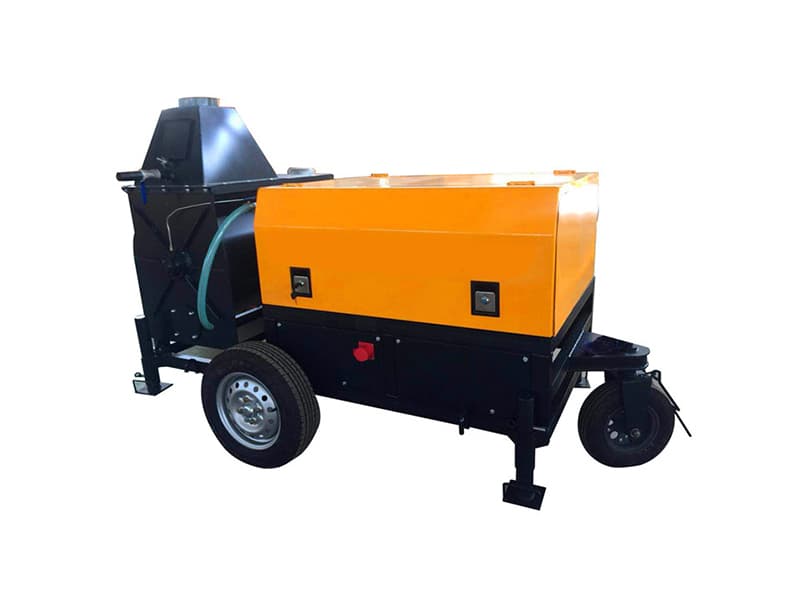
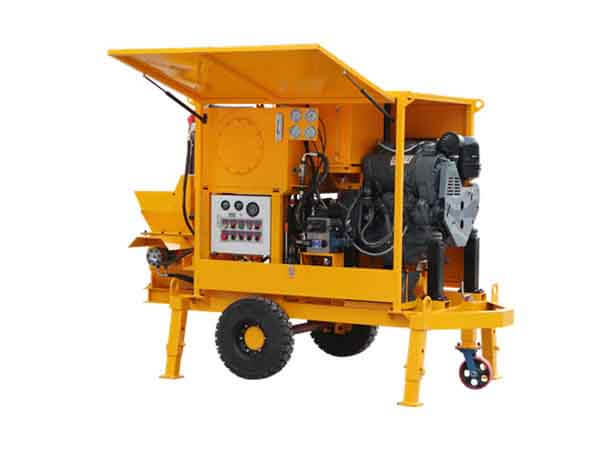
The dry gunning machine is specialized equipment designed for refractory repairs. Its core function involves pneumatically conveying dry refractory materials and projecting them at high velocity onto the repair site, forming a dense, robust refractory lining to achieve rapid restoration of damaged areas. Its core operating principle relies on pneumatic conveying and high-speed spray forming technology: high-pressure airflow generated by an air compressor creates a negative pressure environment within the conveying pipeline. This draws dry refractory powder from the storage hopper and transports it to the spray gun nozzle, where it mixes with a small amount of atomized water (direct dry spraying is possible under certain conditions). The kinetic energy of the high-velocity airflow forces the refractory material to adhere firmly to the damaged furnace surface. Subsequent high-temperature sintering forms a dense structure that bonds tightly with the original lining.
The key components and functions of the dry gunning machine are as follows: First, the storage hopper holds dry refractory material and is equipped with a mixing device to prevent material caking. Second, the delivery system, comprising a screw conveyor and delivery pipes, ensures stable material transport to the nozzle with precisely adjustable flow rates. Third, the spray nozzle, constructed from high-temperature and wear-resistant materials, allows adjustment of spray angle and range to ensure repair precision. Fourth, the air compressor provides stable high-pressure airflow for material conveyance and spraying, with its pressure parameters directly impacting spraying effectiveness. Fifth, the control system enables precise regulation of parameters like feed rate, air pressure, and spray volume via a touch panel. Some high-end models feature intelligent monitoring modules for real-time feedback on construction status.
III. Why Choose Dry Gunning Machines for Hot Repair of Refractories in Rotary Melting Furnaces?
For the unique operating conditions of rotary melting furnaces, dry gunning machines offer multiple irreplaceable advantages that precisely meet industrial production demands for efficient, low-cost maintenance:
1. No furnace shutdown required, drastically reducing downtime: Dry gunning machines can operate directly on rotary smelting furnaces while they remain at high temperatures (typically ≥800°C), eliminating the need for cooling or shutdown. Compared to traditional cold repair methods, this reduces downtime by over 60%, significantly lowering economic losses from production interruptions. For example, a metallurgical enterprise repaired its rotary smelting furnace using a dry gunning machine, completing a single repair in just 4-6 hours. Traditional cold repairs required 3-5 days, demonstrating a significant improvement in production efficiency.
2. High bonding strength for complex operating conditions: The refractory lining formed by high-velocity spraying bonds tightly with the original furnace lining, achieving bonding strengths exceeding 2.5 MPa. This effectively withstands rotational impacts, material erosion, and thermal shock damage from sudden temperature changes in rotary furnaces. The repaired lining achieves a service life approaching that of a new lining.
3. High material utilization reduces maintenance costs: By precisely controlling spray parameters, the dry gunning machine maintains material loss below 5%, far lower than manual application (20%-30% loss). Additionally, eliminating the need for additional cooling or heating energy reduces overall maintenance costs by 30%-50%.
4. Simplified operation, reduced labor costs: The automated equipment requires only 2-3 operators to complete the entire repair process. Compared to traditional cold repairs demanding multiple workers for coordinated tasks, this significantly reduces manpower requirements while minimizing operational risks in high-temperature environments.
IV. Step-by-Step Application Process of Dry Gunning Machines in Hot Repair of Rotary Melting Furnaces
To ensure repair quality and construction safety, the application of dry gunning machines in hot repairs of rotary melting furnaces must follow a standardized step-by-step process, as detailed below:
1. Pre-Repair Preparation Phase: First, conduct a comprehensive inspection of refractory damage using in-furnace monitoring equipment (e.g., high-temperature endoscopes) to identify key parameters such as damaged areas, surface area, and depth, thereby formulating a targeted repair plan. Second, clean the damaged surface of slag, dust, and loose refractory materials to ensure the repair surface is clean and dry, providing a solid foundation for material adhesion. Finally, select suitable dry refractory materials (e.g., high-alumina, magnesia, silicon carbide) based on operating conditions like furnace temperature and material properties, ensuring moisture content ≤1% to prevent clumping or poor adhesion during spraying.
2. Equipment Commissioning Phase: Position the dry gunning machine in a safe area near the furnace access port. Connect the delivery pipeline, air compressor, and control system. Verify the sealing integrity and operational stability of all equipment components. Focus on adjusting the airflow pressure (typically set at 0.6-0.8 MPa) and material feed rate (adjusted to 50-150 kg/h based on the repair area) to ensure parameters align with repair requirements. Conduct test spraying to inspect material distribution uniformity and bonding effectiveness, then fine-tune parameters based on the test results.
3. Hot Spraying Construction Phase: Operators wearing high-temperature protective gear control the spray gun nozzle via remote operation or a protective platform. Aim the nozzle at the damaged area, maintaining a distance of 0.8-1.2m between the nozzle and repair surface. Spray in a uniform circular trajectory to ensure consistent repair layer thickness (typically 50-100mm per pass; for thicker linings, multiple passes may be required with sufficient curing time between layers). During spraying, dedicated personnel monitor repair progress in real-time via monitoring equipment, promptly adjusting spray angles and parameters to prevent missed areas or material buildup.
4. Post-Repair Inspection Phase: After spraying, maintain normal furnace operation to allow the repair layer to naturally sinter and cure under high temperatures (typically requiring 2-4 hours). Upon curing completion, inspect the repair layer's surface flatness, density, and bonding with the original lining using a high-temperature endoscope. Perform localized re-spraying if necessary. Continuously monitor the repaired furnace's operating parameters (e.g., temperature, pressure, rotational speed) for 24 hours. Only resume normal production load after confirming the repair meets specifications.
Under the demands of industrial high-efficiency continuous production, the dry gunning machine has become the core equipment for refractory maintenance in rotary melting furnaces. Its key advantages—hot repair capability, energy efficiency, and strong bonding—significantly shorten repair cycles, reduce costs, and ensure production continuity. For industries such as metallurgy, glass, and cement, selecting suitable models and implementing standardized application practices are crucial for enhancing equipment operation and maintenance standards while reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Looking ahead, intelligent and green technologies will drive application upgrades for dry gunning machines in this field. Enterprises are advised to select reputable suppliers based on their specific operating conditions, leveraging specialized equipment and standardized construction to enhance furnace operational efficiency and lifespan. For customized model selection or technical support, consult professional suppliers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can dry gunning machines be used for all types of rotary melting furnaces? Answer: They are generally compatible with most rotary melting furnace types (e.g., metallurgical furnaces, glass furnaces, cement kilns), but require selection of appropriate equipment models and refractory materials based on furnace operating temperatures and material characteristics. For furnaces with special structures (e.g., irregular inspection ports, oversized furnace bodies), customized designs can be requested from manufacturers.
2. What is the service life of the refractory lining after repair by a dry gunning machine? Answer: The service life of the repaired lining primarily depends on operating conditions and material quality. Under typical metallurgical or glass furnace conditions, it can reach 12-18 months, approaching the lifespan of a new lining. In milder conditions (e.g., low-temperature melting, minimal material erosion), service life can extend beyond 20 months.
3. How should one select the appropriate dry refractory spray coating? Answer: Selection should be based on furnace operating temperature (e.g., high-alumina or magnesia materials for high-temperature furnaces), material erosion characteristics (e.g., alkali-resistant materials for alkali metal erosion), and stress conditions at the repair site (e.g., high-wear-resistant silicon carbide materials for areas with severe erosion). It is recommended to consult supplier technicians for material selection to ensure compatibility with equipment and operating conditions.
4. Do equipment suppliers provide on-site operational training? Answer: Reputable suppliers offer complimentary on-site training covering equipment installation, commissioning, parameter settings, construction standards, and troubleshooting. Some suppliers also conduct periodic technical follow-ups to ensure operators master equipment operation proficiently.


.jpg)









.jpg)