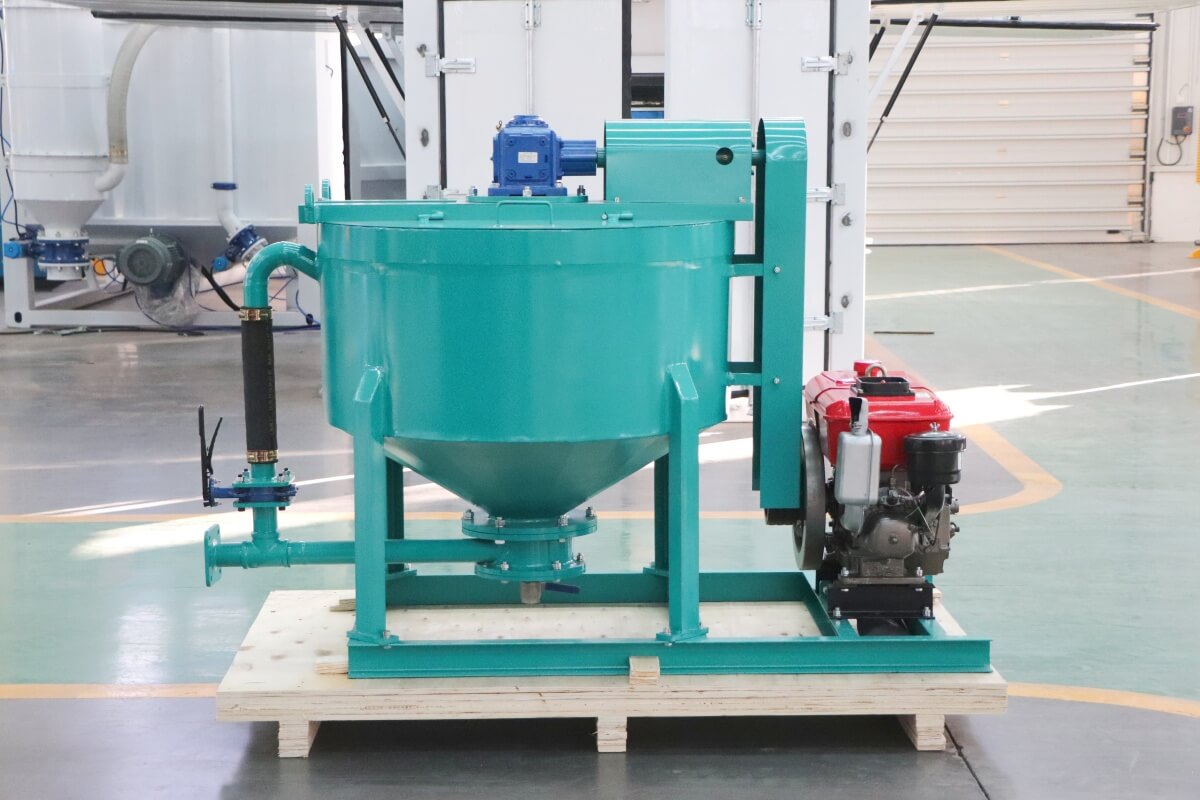
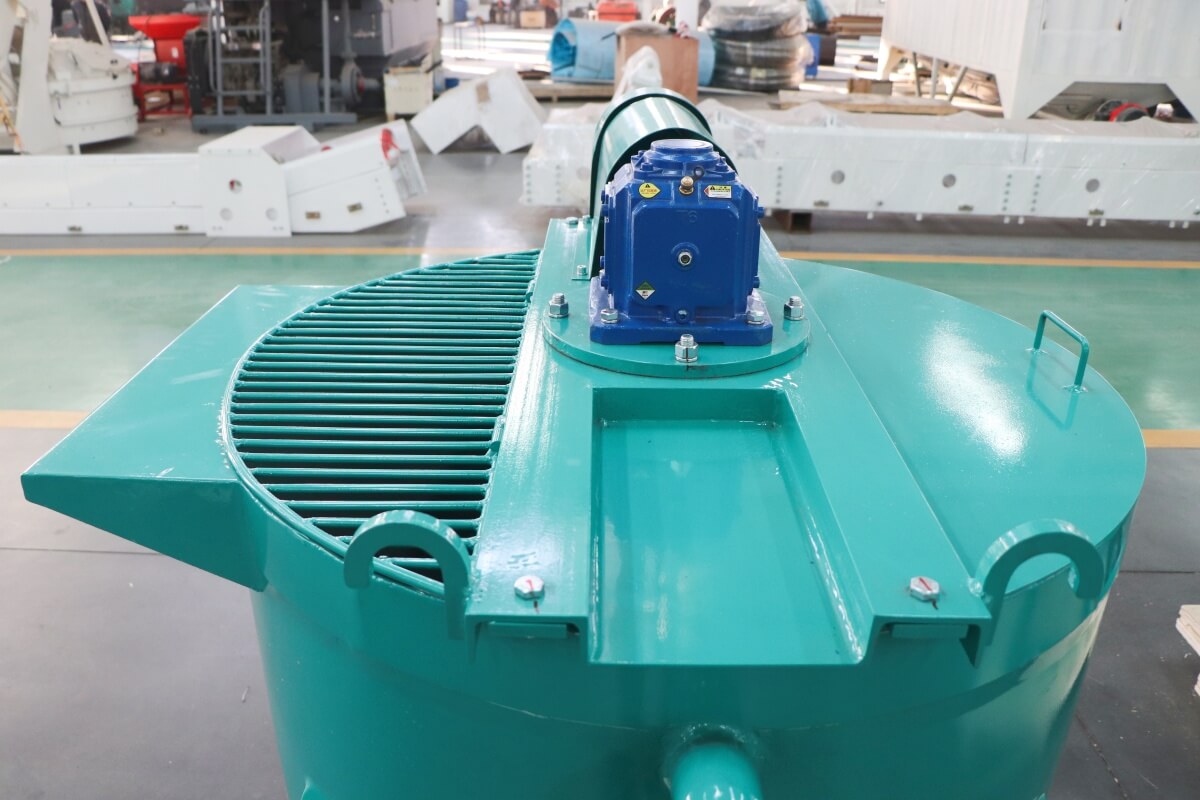
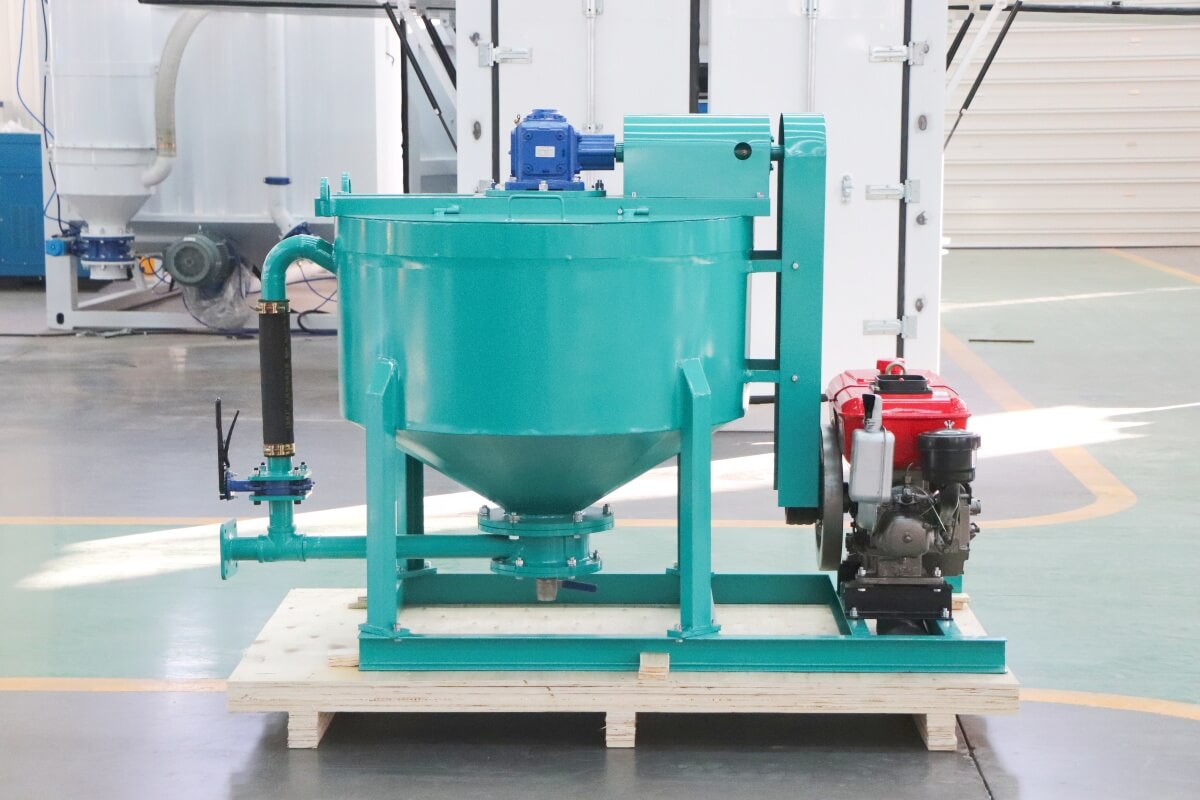
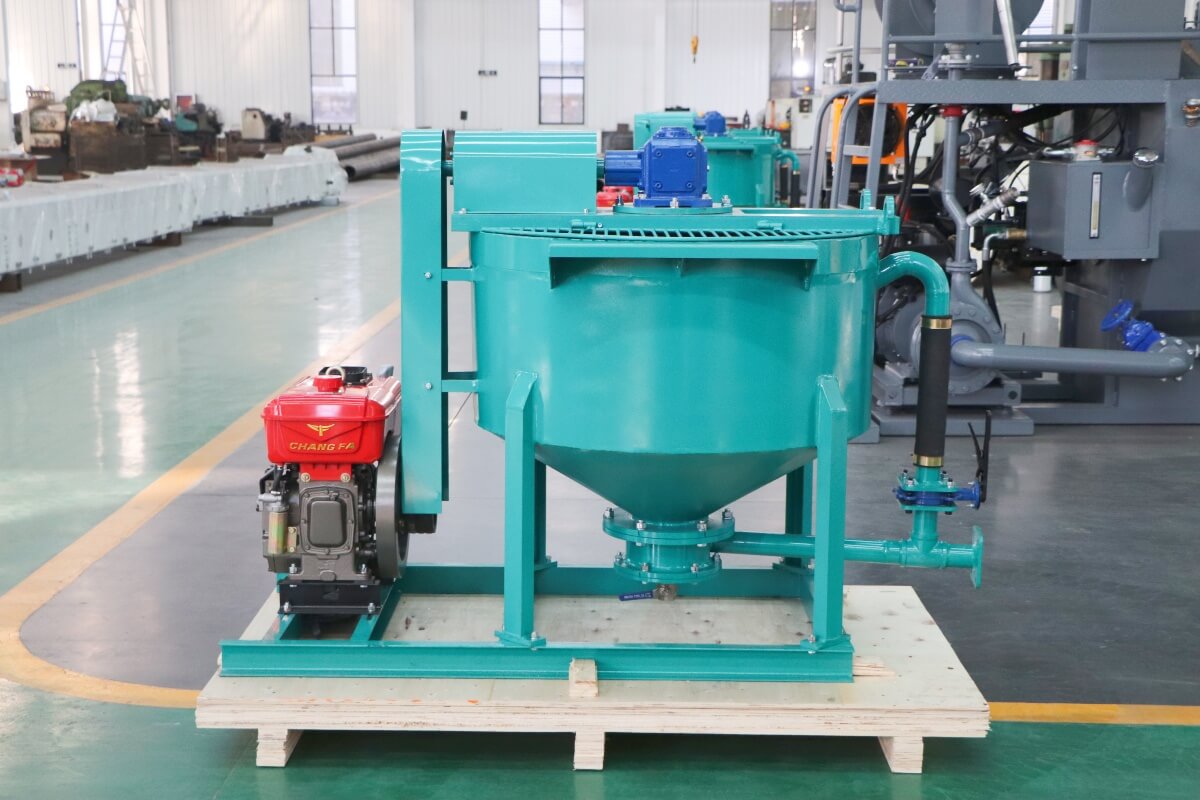
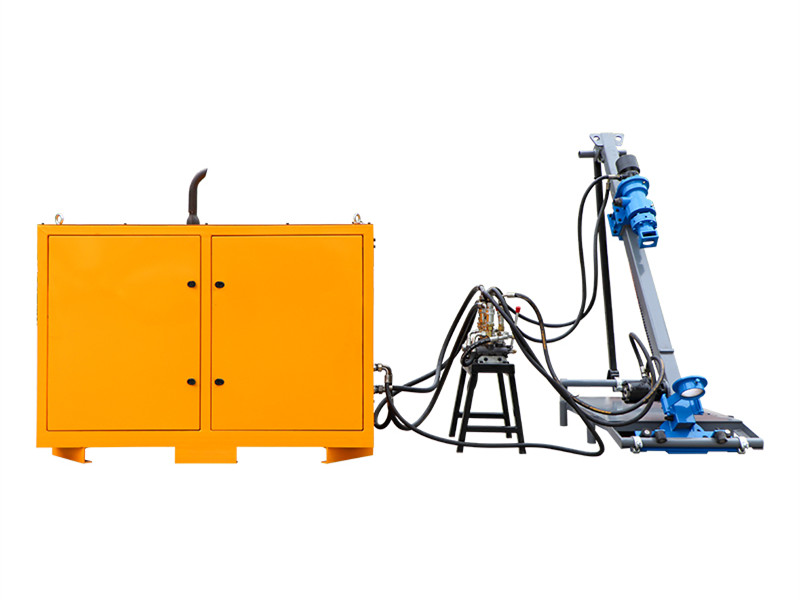
Dams form the backbone of water conservancy projects, with their structural integrity directly impacting watershed safety and water resource management. Long-term operation often leads to concrete cracking, seepage, and foundation settlement—issues primarily addressed through grouting reinforcement. Leveraging its high-efficiency mixing capabilities, the high-shear cement grout mixer has become essential for ensuring dam reinforcement quality. This article provides an in-depth analysis covering its technology, selection criteria, and practical applications.
I. Understanding grout mixer technology
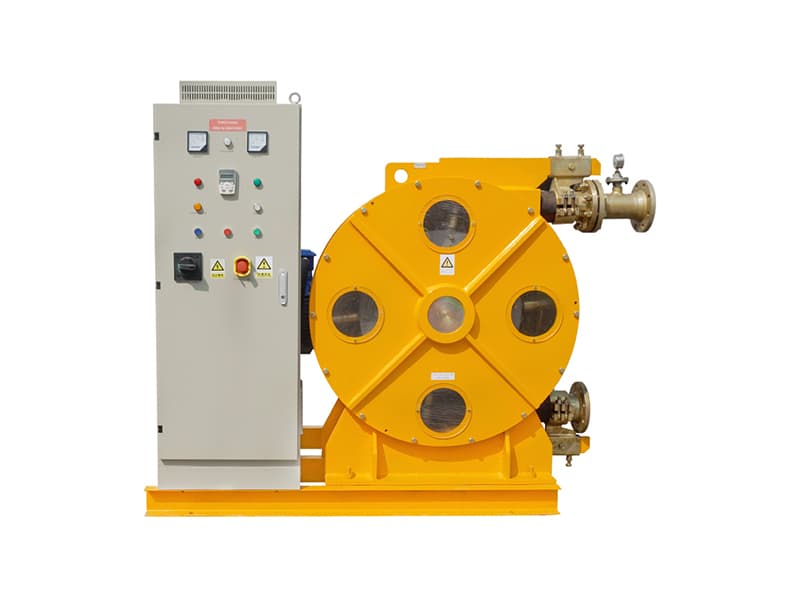
Grout mixers serve as the core equipment for preparing high-performance grouting materials in dam reinforcement projects. Their technical proficiency directly determines the uniformity, flowability, and strength stability of the grout body. Currently, grout mixers commonly used in engineering projects are primarily categorized into two types: traditional mixing equipment and high-shear mixing equipment: Traditional mixers predominantly employ screw or paddle agitation modes, suffering from issues such as low mixing efficiency and uneven particle dispersion. In contrast, high-shear grout mixers utilize specialized shear structures to achieve deep integration of cement particles with water and additives, meeting the stringent requirements for grouting materials in dam reinforcement.Core components of industrial-grade grout mixers include high-power drive motors, precision shear mixing chambers, high-efficiency impeller assemblies, and intelligent control systems. For dam engineering applications, such equipment must meet three core requirements: First, it must comply with the performance standards outlined in the Technical Specifications for Grouting Construction in Hydraulic and Hydroelectric Engineering, ensuring the 28-day compressive strength of the grout body does not fall below the design value. Second, it must possess stable continuous operation capabilities to accommodate the large-scale grouting demands of dam reinforcement projects. Third, it must adapt to complex construction site environments, featuring interference resistance and ease of operation.
II. High shear grout mixer working principle
The core advantage of high-shear grouting mixers stems from their unique operating mechanism. Essentially, they break down the agglomerated structure of cement particles through mechanical shear forces, achieving microscopic uniform mixing of materials. The specific working process can be divided into three key stages: First, the motor drives the impeller to rotate at high speed (typically reaching 1500-3000 rpm), creating a strong turbulent flow field within the mixing chamber; Second, the shear teeth at the impeller edges generate extremely high localized shear rates, breaking cement lumps into minute particles. Finally, the recirculating mixing design ensures materials pass through the shear zone multiple times within the mixing chamber, guaranteeing thorough dispersion and uniform blending of components like cement, water, and admixtures.Compared to conventional mixers, high-shear technology effectively eliminates the “pseudoplasticity” phenomenon in cement grout, preventing incomplete hydration due to internal cement particle agglomeration. The resulting grout exhibits excellent microscopic uniformity. When injected into dam cracks or voids, it forms a dense cementitious structure, significantly enhancing the water resistance and load-bearing capacity of the reinforced sections. Furthermore, high-shear mixing achieves high energy conversion efficiency, reducing preparation time for the same grout volume by 30%-50% compared to conventional equipment, thereby substantially improving dam reinforcement construction efficiency.
III. How to choose the right grout mixer for your dam consolidation project
Selecting the appropriate high-shear grouting mixer requires a comprehensive assessment based on the specific requirements of the dam project, focusing on the following four core factors:1. Project Scale and Grouting Volume Requirements
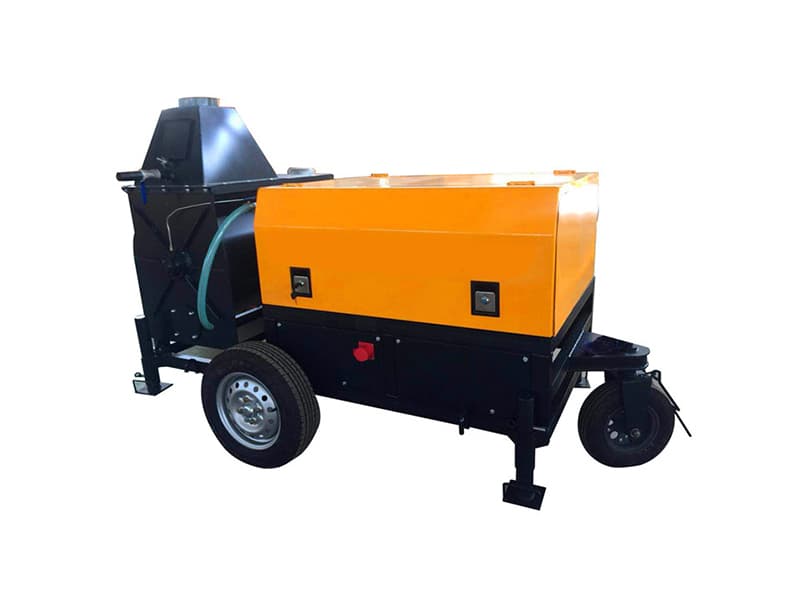
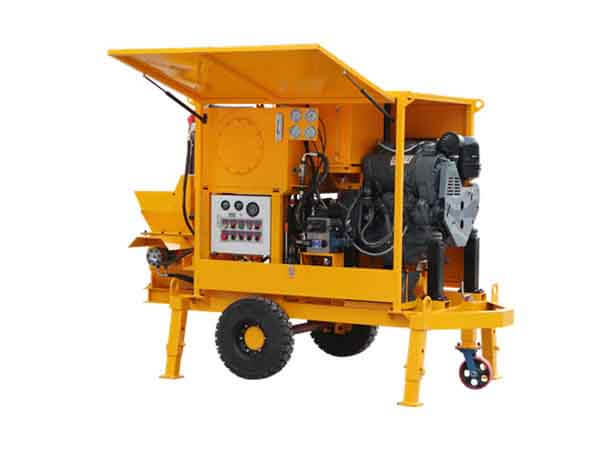
For large-scale gravity dams, arch dams, and similar structures, opt for high-capacity continuous high-shear mixers (single-batch capacity ≥5m³) to meet daily grouting demands of hundreds of cubic meters. For small-to-medium dam reinforcement or localized repair projects, mobile compact high-shear units (mixing capacity 1-3m³) offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness.2. Compatibility with Grouting Material Properties
Grouting formulations vary significantly across different dam reinforcement scenarios:- Cement-water glass dual-liquid grouting requires dual-chamber independent shear mixers to prevent premature reaction between the two slurries; Ultrafine cement grouting requires a mixer shear gap ≤0.5mm to ensure complete dispersion of ultrafine particles; Grouting materials incorporating additives like bentonite or water-reducing agents necessitate equipment with variable-frequency speed control to adjust shear rates according to material viscosity characteristics.
3. Core Technical Parameter Comparison
Key parameters include: shear rate (≥10⁴ s⁻¹), motor power (matched to mixing volume, typically ≥15 kW), mixing uniformity (coefficient of variation ≤5%), and operational stability (≥8 hours of continuous fault-free operation). Additionally, focus on wear resistance—mixing chambers and impellers should utilize high-chromium alloy or ceramic-coated materials to extend service life.4. Adaptation to Site Conditions
For elevated operations like dam crests or shoulders, select lightweight equipment (total weight ≤2t) with lifting fixtures. For underwater grouting or humid environments, ensure IP65 waterproof protection. Remote projects should prioritize fuel-efficient, low-maintenance models to reduce operational costs.Additionally, avoid common selection pitfalls: blindly pursuing high capacity while neglecting actual grouting volume requirements leads to low equipment utilization; focusing solely on price while ignoring core component materials and machining precision results in skyrocketing maintenance costs. It is recommended to prioritize equipment suppliers with certified qualifications for water conservancy projects, referencing successful case studies from similar dam constructions.
IV. Grout mixing solutions for dam consolidation application
The application of high-shear grouting mixers requires tailored mixing plans based on dam structure types and reinforcement objectives:1. Customized Solutions for Different Dam Types
• Concrete Gravity Dams: For vertical crack reinforcement, employ a “high-shear pre-mixing + on-site secondary mixing” approach. The pre-mixing stage ensures thorough dispersion of cement particles, while secondary mixing guarantees slurry homogeneity prior to grouting. Recommended mixing speed: 2200 rpm; shearing time: 3-5 minutes.• Earth or rock-fill dams: Focuses on resolving seepage issues by preparing cement-bentonite composite grout using high-shear mixers. Adjusting impeller speed (1800-2000 rpm) controls slurry viscosity between 50-80 mPa·s, ensuring effective penetration into dam pore spaces.
• Foundation reinforcement projects: For fault zones and fractured belts, employ a twin-shaft high-shear mixer to simultaneously prepare cement slurry and solidifying agents. Precisely control the mixing ratio of both materials to enhance foundation bearing capacity and slip resistance.
2. Optimized Mixing Process for Grouting Materials
Mixing quality directly impacts reinforcement effectiveness. Adhere to the principle of “Precise Proportioning - Segmented Mixing - Real-time Monitoring”: First, an electronic metering system controls the mixing error of cement, water, and admixtures to ≤±1%. Second, a staged mixing process of “dry mixing for dispersion - wet mixing for integration” is adopted: dry cement powder undergoes high-shear dry mixing for 1 minute, followed by adding water and admixtures for 3-4 minutes of mixing. Finally, monitor slurry properties in real-time using an online viscometer, dynamically adjusting mixing speed or duration based on readings.3. On-site Construction Operating Standards
Field use of high-shear mixers must strictly adhere to these guidelines: Ensure equipment is level and securely fixed during installation to prevent vibration from compromising mixing quality; Inspect the shear gap before operation. If wear exceeds 1mm, promptly adjust or replace the impeller. Avoid overloading during mixing. When slurry viscosity exceeds 1.5 times the design value, stop the machine to investigate material ratios or equipment malfunctions. After construction, promptly flush the mixing chamber with clean water to prevent cement scaling that could affect subsequent use.V. Grouting and Cement: Fundamental Differences and Engineering Application Boundaries
In dam reinforcement projects, “grouting” and “cement” are two easily confused concepts with distinct fundamental differences: Cement is a single cementitious material primarily composed of minerals such as tricalcium silicate and dicalcium silicate. Grout, however, is a composite slurry formed by mixing cement, water, aggregates, admixtures, and other components in specific proportions, with its properties precisely controlled according to reinforcement requirements.Specifically, grout used for dam reinforcement must meet three core requirements: First, it must possess sufficient fluidity to penetrate micro-cracks (width ≥ 0.1mm) within the dam structure under pressure. Second, its setting time must be controllable, with an initial setting time aligned with construction schedules (typically 2-8 hours) to prevent premature setting during placement. Third, post-curing properties must exhibit high compressive strength (≥30MPa), water resistance rating (≥P8), and bond strength (≥2.5MPa). Plain cement mixed with water alone suffers from poor flowability and excessively rapid setting, failing to meet grouting construction requirements.
In engineering practice, strict application boundaries must be maintained: cement is primarily used for pouring main dam structures or surface repairs, while grouting is applied to concealed works such as filling internal dam cracks, foundation consolidation, and impermeable curtains. Misusing plain cement slurry for grouting can lead to ineffective penetration, shrinkage cracking after curing, and other issues that severely compromise dam reinforcement effectiveness.
VI.What are the advantages of cement grout mixer?
Compared to traditional mixing equipment, high-shear cement grout mixers offer five distinct advantages in dam reinforcement projects:1. Significantly Enhanced Grouting Quality
Through high-intensity shear action, cement particle dispersion can be reduced to below 50μm, improving slurry uniformity by over 40%. After curing, the porosity of the grout body is ≤3%, with water resistance and compressive strength increased by 35% and 25% respectively, effectively extending the service life of reinforced dams.2. Substantially Enhanced Construction Efficiency
High-shear mixing reduces batch mixing time to 1/2–2/3 of conventional equipment. For projects with an average daily grouting volume of 100m³, this reduces required mixing units by 30%, shortens construction duration by 15–20%, and lowers labor and equipment rental costs.3. Exceptional Adaptability
Flexible adjustment of mixing parameters accommodates diverse grouting materials including cement slurry, cement-water glass dual-liquid slurry, ultra-fine cement slurry, and polymer-modified slurry. This meets technical requirements for different dam sections and reinforcement objectives, enabling a single unit to cover all grouting mixing operations across the project.4. Stable and Reliable Operation
Features industrial-grade core components with a mixing chamber and impeller wear life ≥8000 hours and a failure rate ≤2%. Designed to withstand harsh dam construction environments including high temperatures, humidity, and dust, ensuring continuous grouting operations.5. Enhanced Safety Assurance
Equipped with an intelligent monitoring system that tracks parameters like slurry viscosity, mixing temperature, and motor load in real time. It automatically triggers alarms and shuts down upon anomalies, preventing reinforcement failures caused by slurry quality issues. Additionally, the equipment features user-friendly operation design, reducing labor intensity and operational complexity for construction personnel.Dam reinforcement projects are critical measures for ensuring the long-term safe operation of water conservancy facilities. As core construction equipment, the performance of high-shear cement grout mixers directly determines grouting quality and reinforcement effectiveness. During project implementation, high-shear mixing equipment must be scientifically selected based on factors such as project scale, grouting material characteristics, and site conditions, while strictly adhering to optimized mixing processes and operational standards.
Investing in premium high-shear cement grouting mixers significantly enhances construction quality and efficiency in dam reinforcement projects, providing equipment assurance for subsequent projects and delivering dual benefits of economy and safety. It is recommended that project owners prioritize suppliers with proven technology, strong reputation, and excellent service. Conducting on-site trial mixing and performance testing to verify equipment suitability will provide reliable assurance for dam safety.


.jpg)









.jpg)