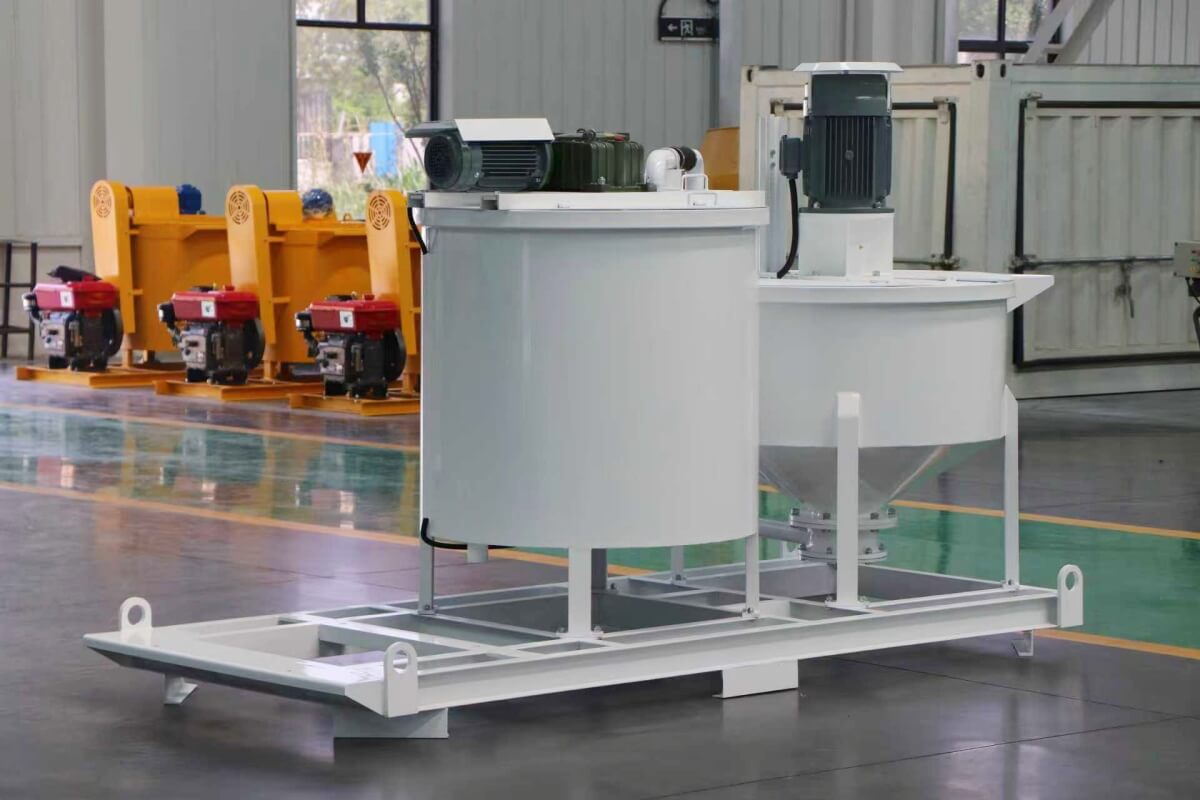
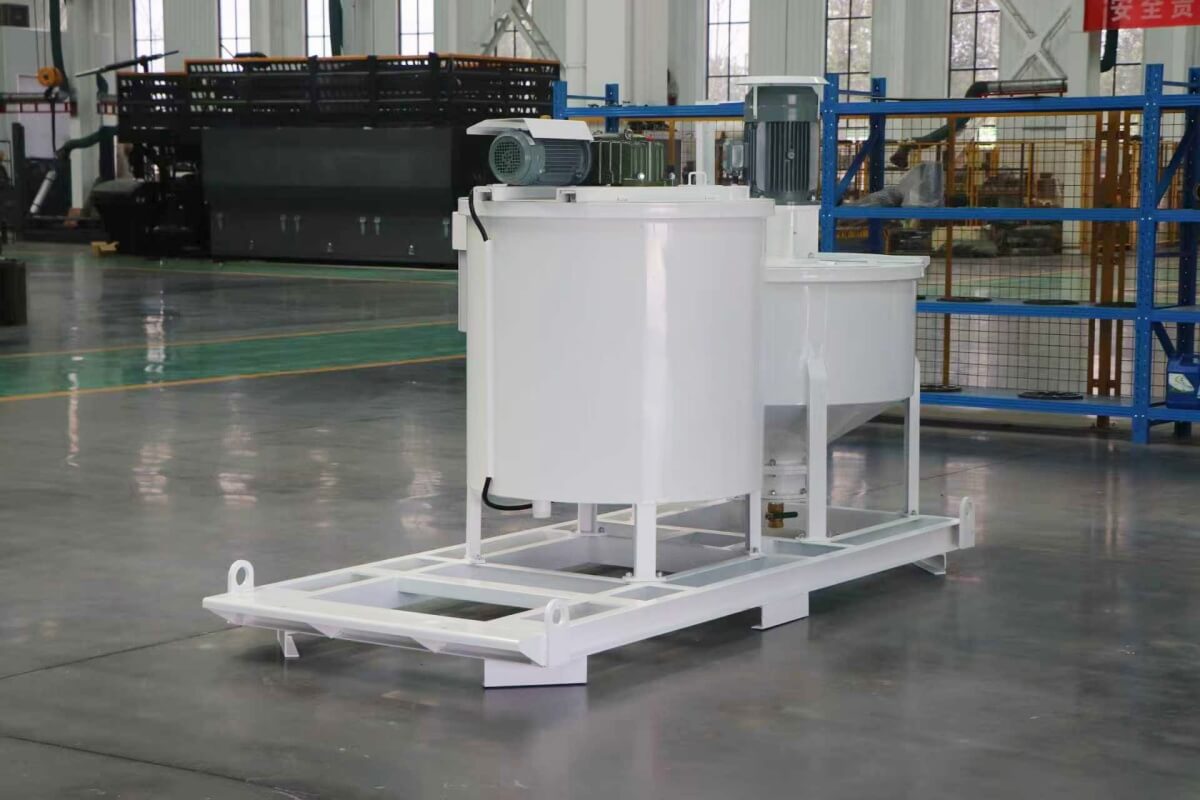
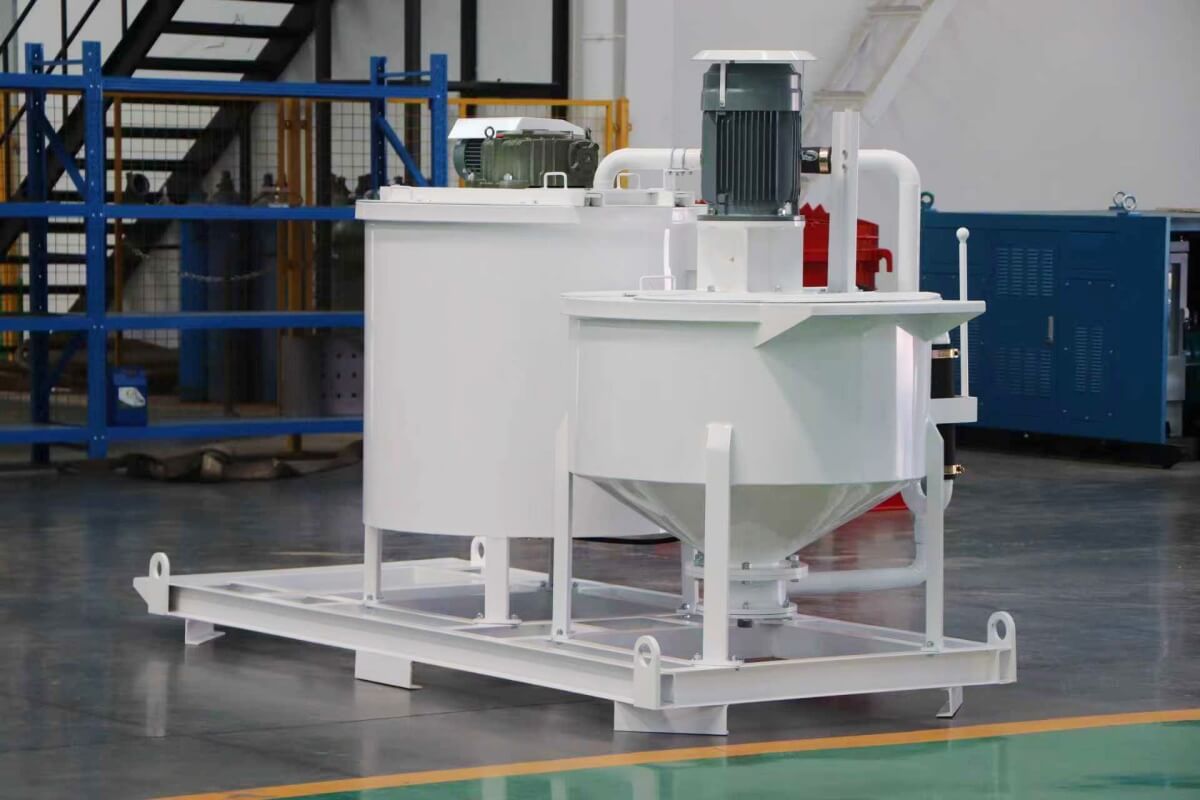
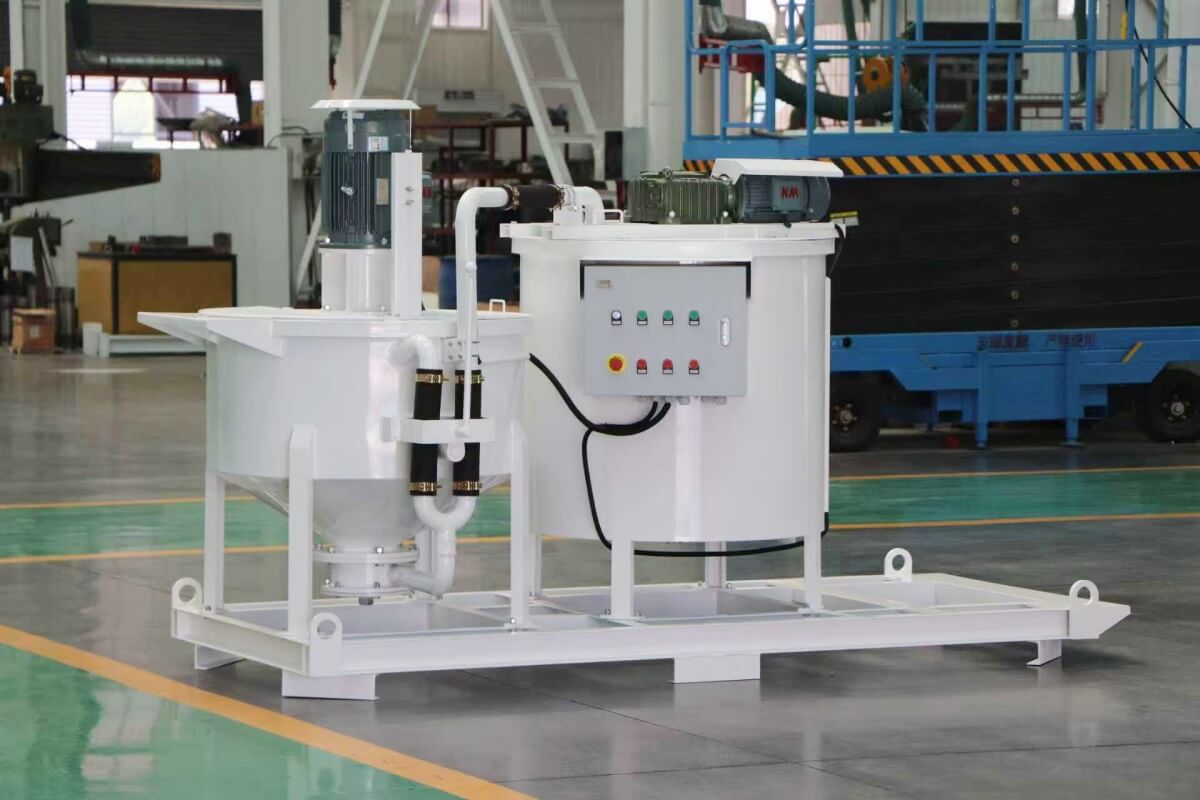
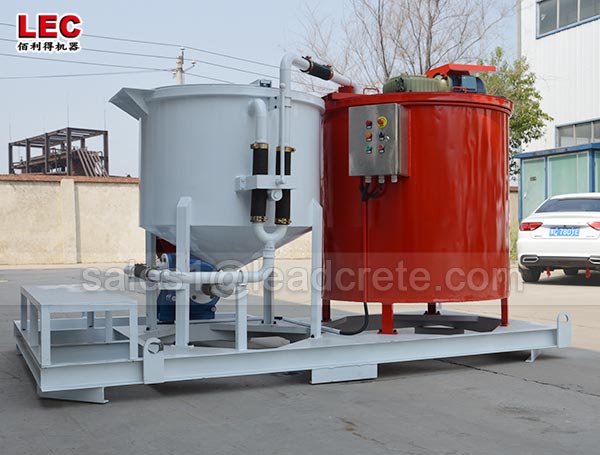
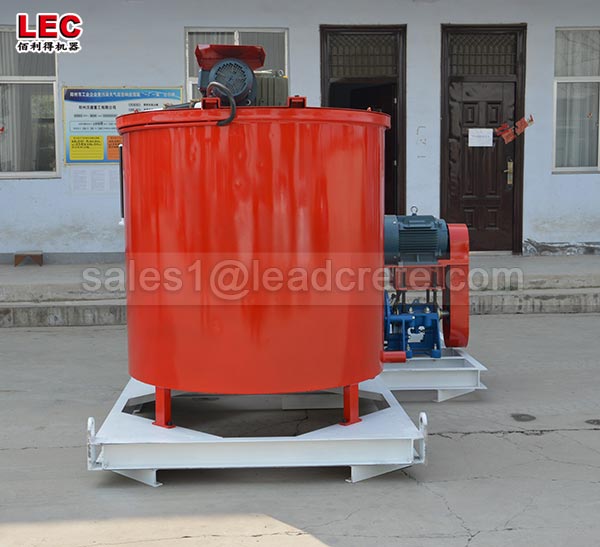
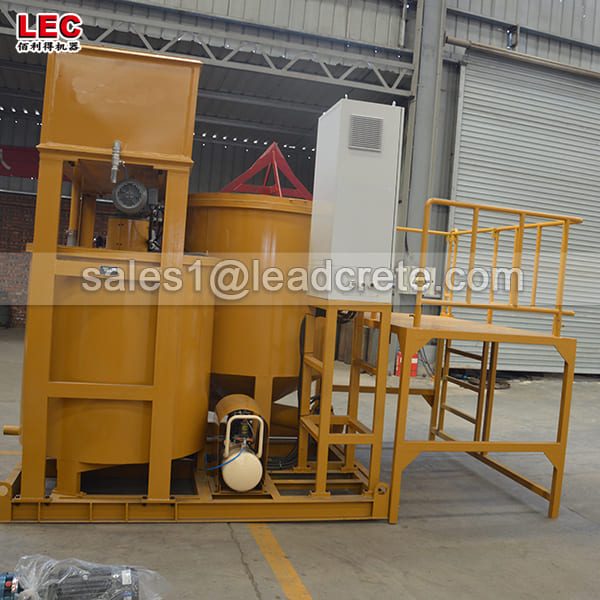
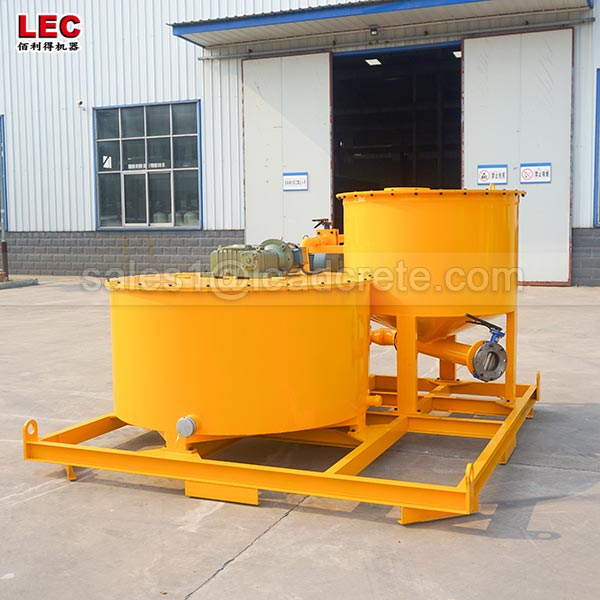
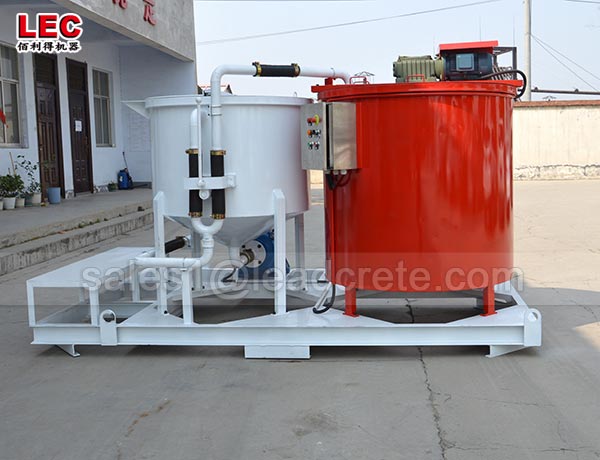
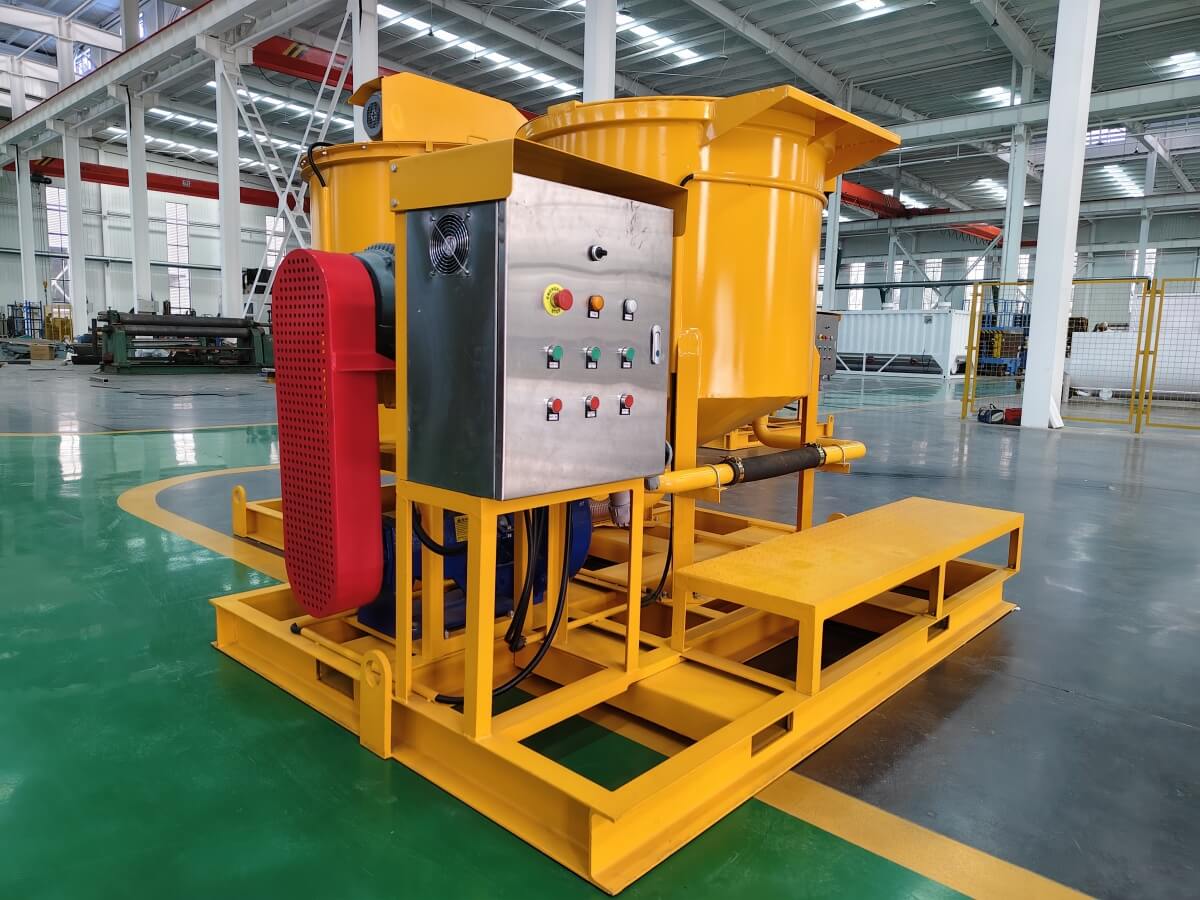
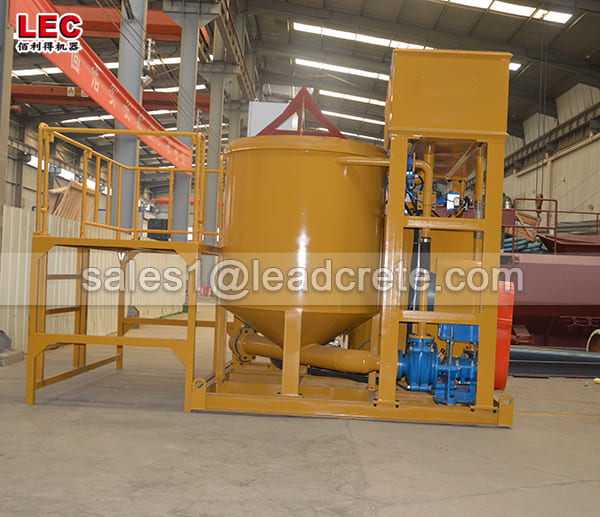
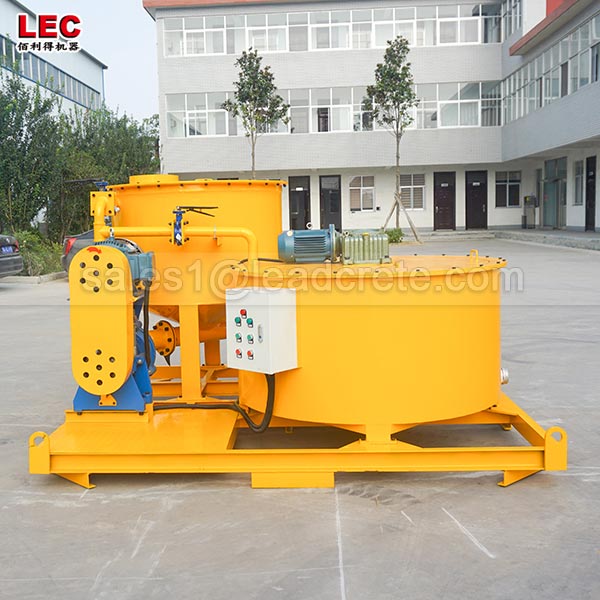
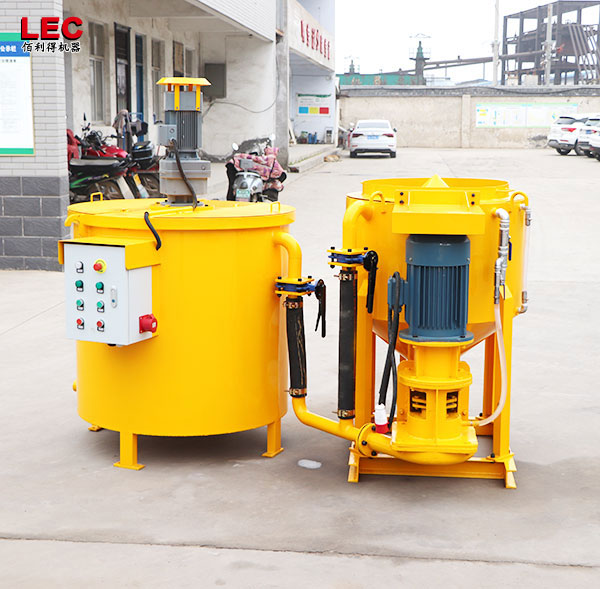
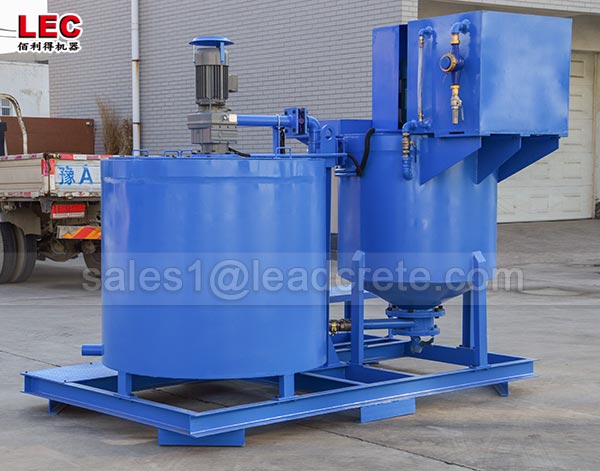
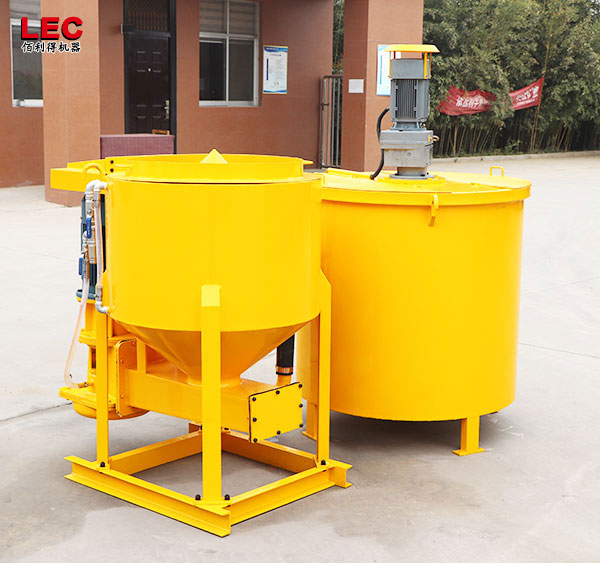
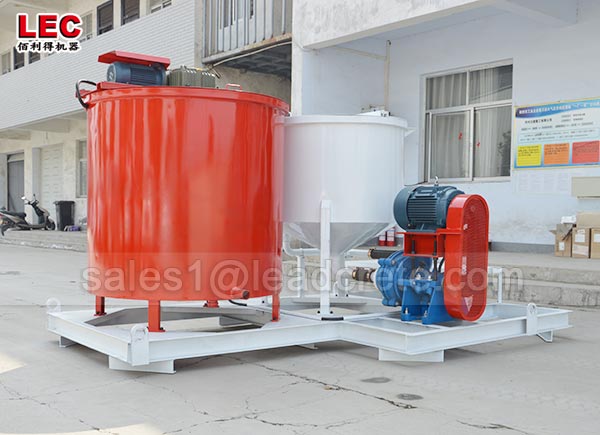
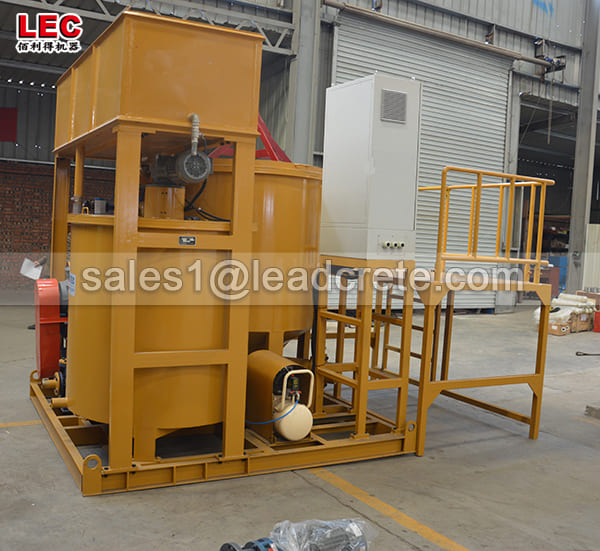
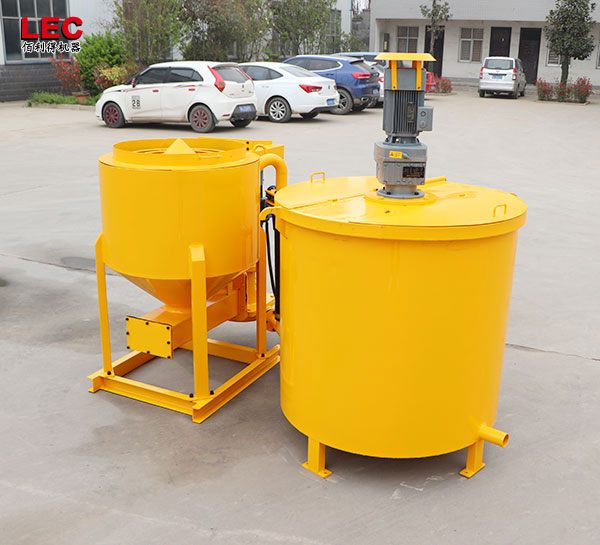
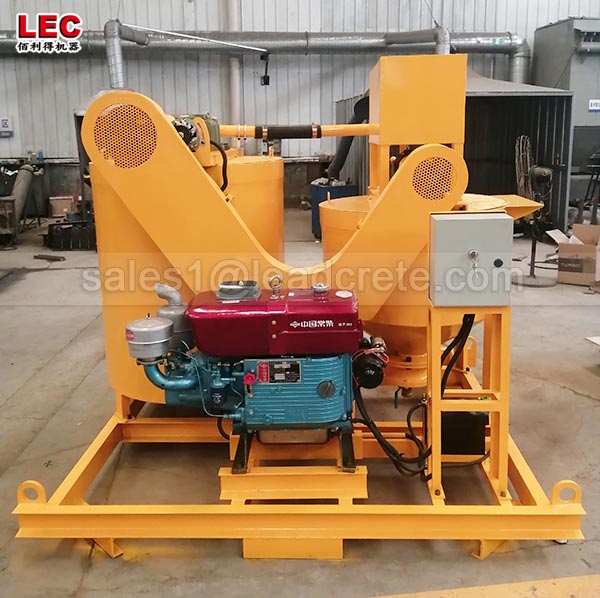
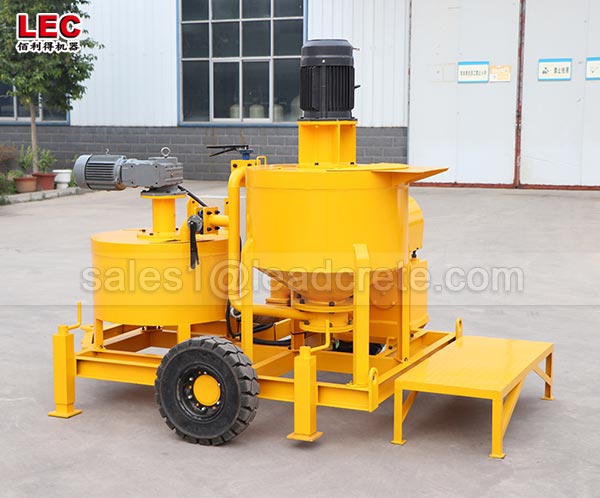
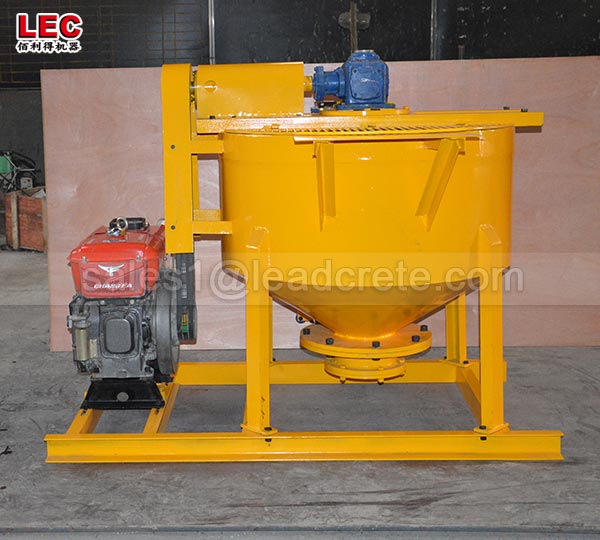
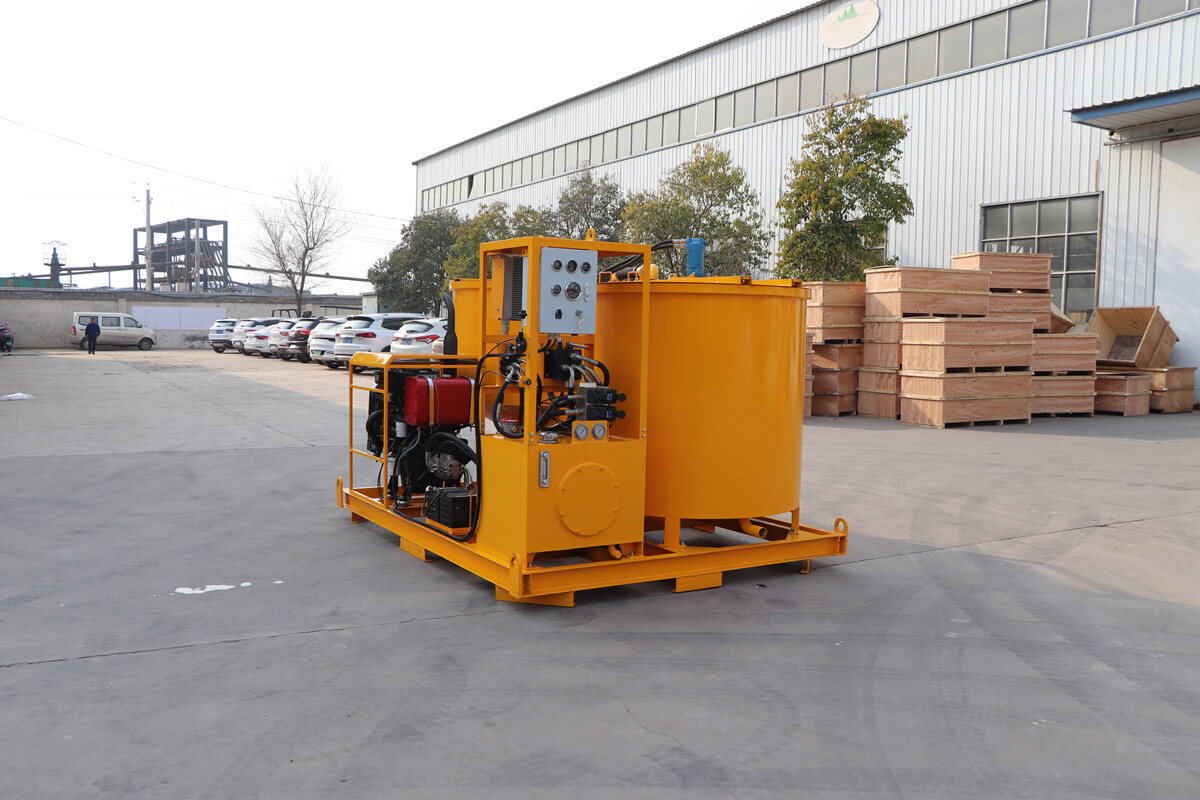
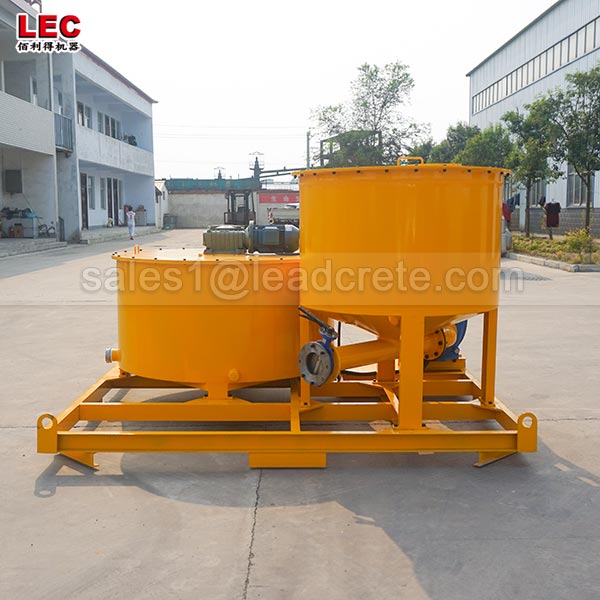
Grout mixer for ground engineering application
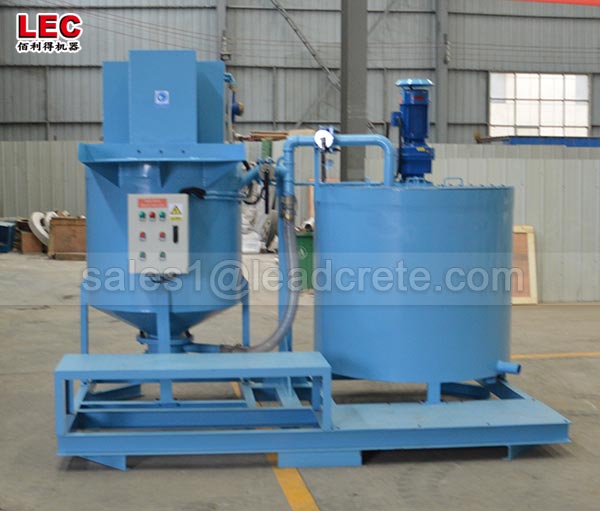
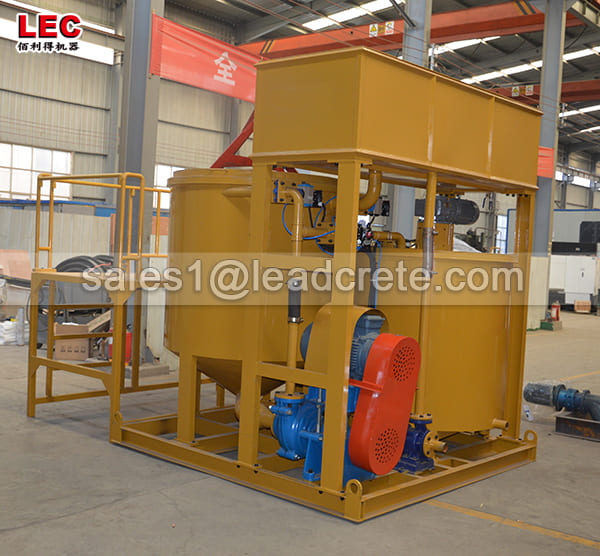
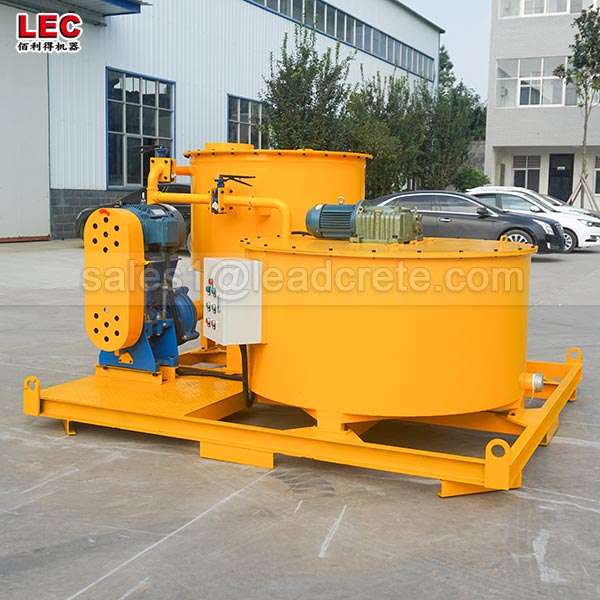
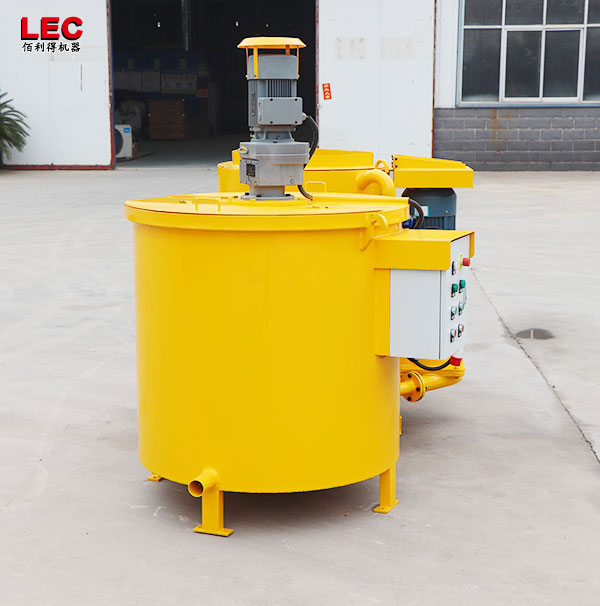
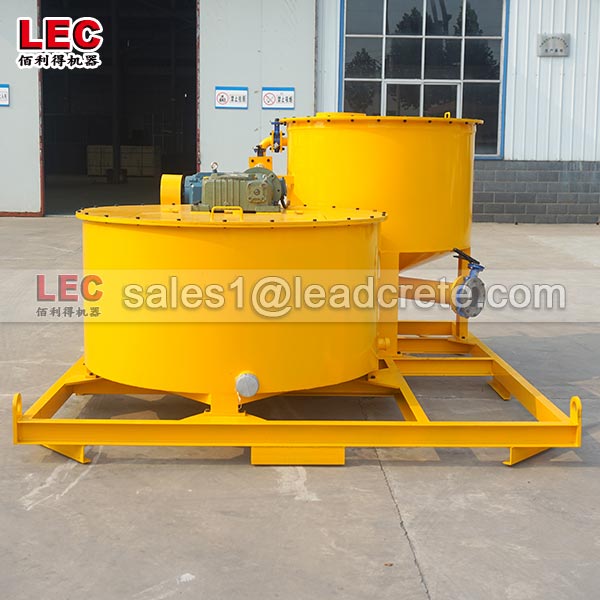
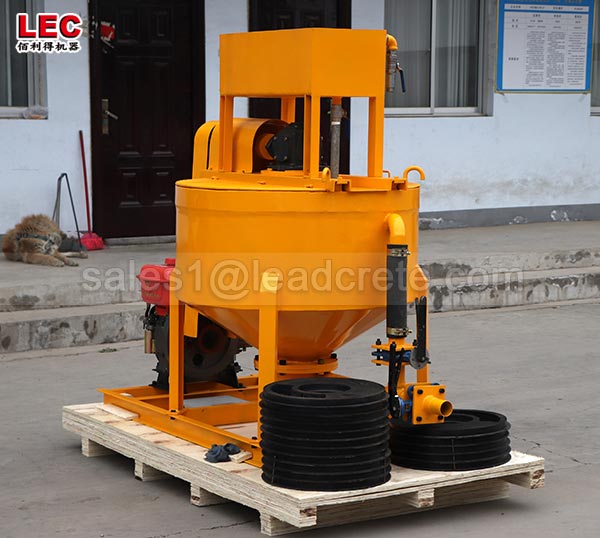
A grout mixer for ground engineering applications is a critical piece of equipment used to prepare high-quality, homogeneous grouts for soil and rock stabilization, foundation support, water control, and deep excavation projects. These mixers are engineered to handle a wide range of materials—including cement, bentonite, microfine cements, fly ash, polymers, and chemical grouts—with precision and consistency.
Grout mixer for ground engineering working principle:
High-Speed Shear Mixing
A high-shear zone is formed between the rotor and stator. The speed differential (typically 1450 to 12,000 rpm) generates intense shear forces, pulverizing solid particles such as bentonite and cement and evenly dispersing them in the water.
The vortex circulation design ensures a continuous flow of the slurry within the mixing tank, eliminating dead zones and achieving uniform mixing.
Multi-Stage Shear and Particle Size Control
High-end equipment utilizes a multi-stage rotor-stator structure. The slurry passes through multiple shear zones, gradually refining the particle size, ultimately forming a stable slurry with an extremely narrow particle size distribution.
For example, ultra-high-speed shear technology can achieve uniform dispersion of submicron particles (<1μm), significantly improving slurry stability.
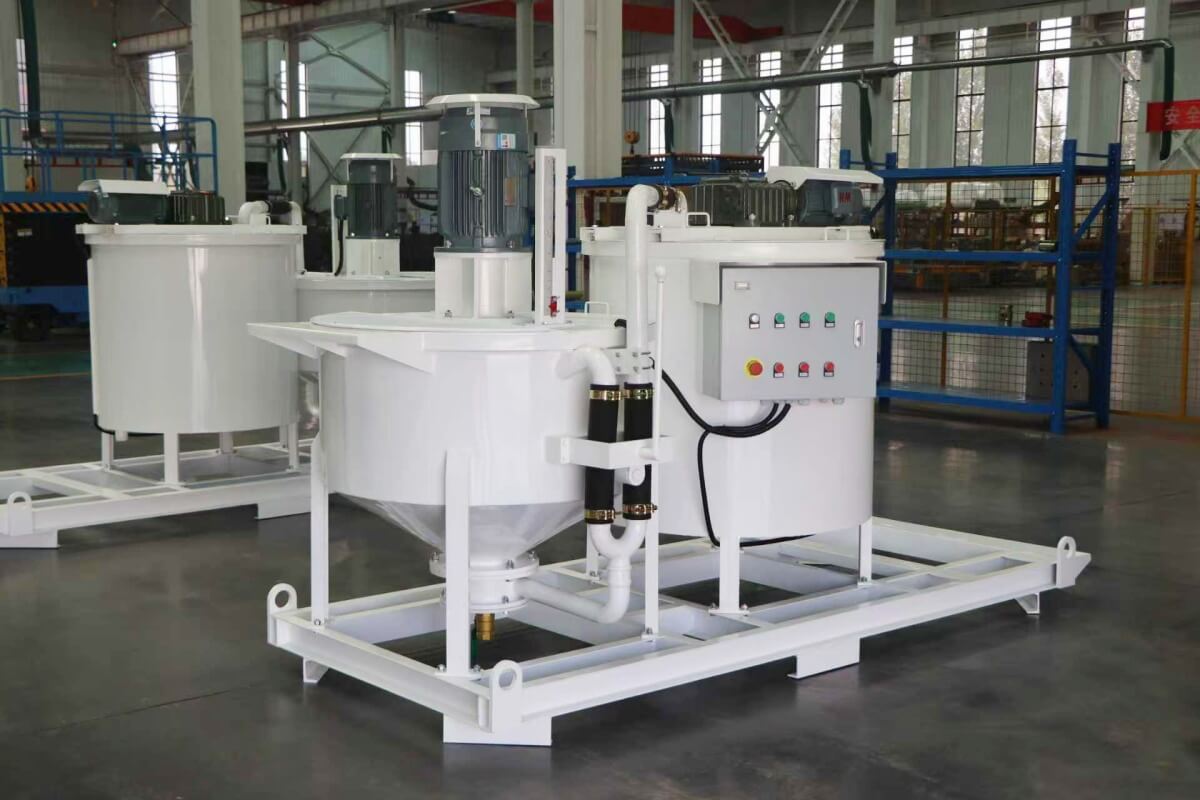

Common grout mixer for ground engineering applications:
| Application | Purpose | Grout Type Used |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Nailing & Anchoring | Reinforce slopes and retaining walls | Cementitious grout (typically 0.5:1 to 0.6:1 w/c ratio) |
| Jet Grouting (CGI, FGI) | Create soil-cement columns for ground improvement | High-strength cement slurry, often with bentonite additive |
| Compensation Grouting | Prevent settlement during tunneling | Low-shrink, controlled low-strength material (CLSM) or cement-bentonite |
| Permeation & Fracture Grouting | Strengthen weak soils or seal water paths | Cement, microfine cement, or chemical (silicate/resin) grouts |
| Diaphragm / Slurry Walls | Trench support during excavation | Bentonite or cement-bentonite slurry |
| Tunneling (TBM & NATM) | Face stabilization, backfill grouting | Cement, two-component chemical grouts |
| Ground Freezing Support | Seal annular spaces | Fast-setting cement or chemical grouts |